Klik op een skeletdeel
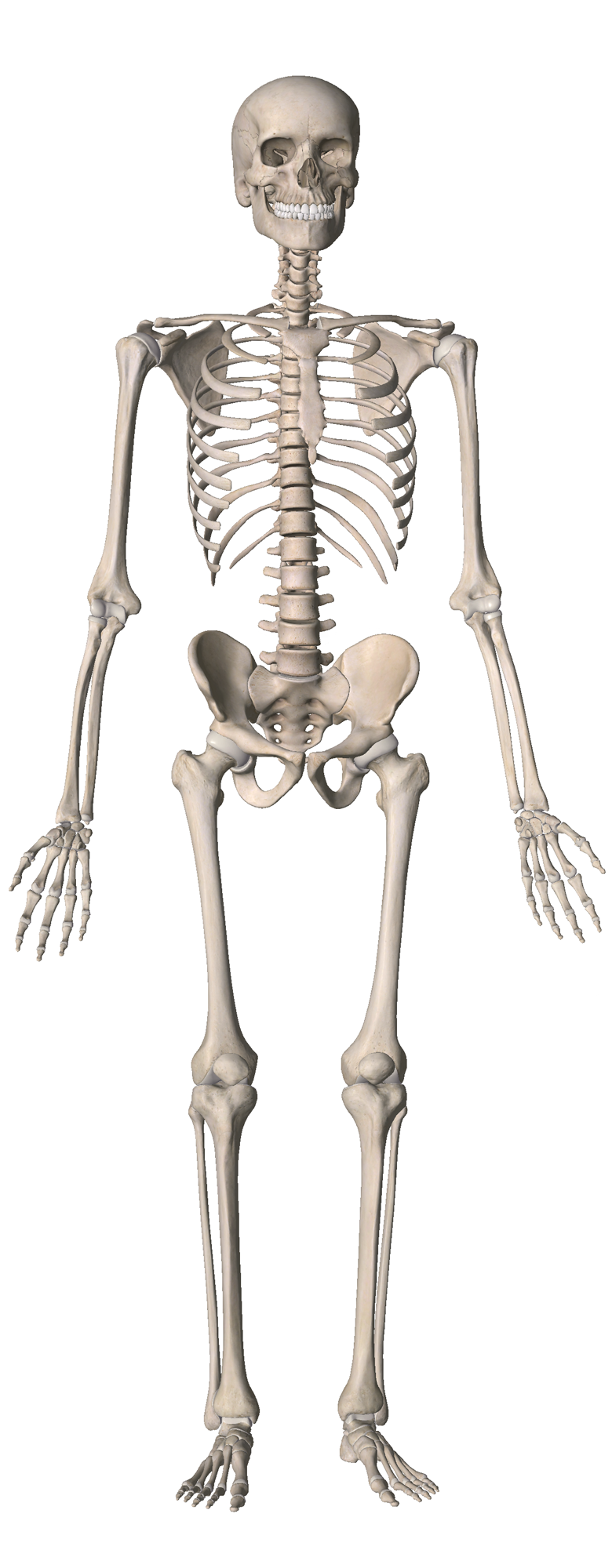
Deze applicatie verschaft informatie over hoe fracturen bij volwassenen behandeld zouden kunnen worden door op het betreffende bot te klikken
Deze applicatie is gemaakt voor artsen en geeft informatie over fractuurbehandeling bij volwassenen. Deze applicatie fungeert niet als protocol, dus kunnen hieraan door patienten of artsen geen rechten ontleend worden. (zie ook de disclaimer)
De tekst is zorgvuldig samengesteld en het is de bedoeling dat er regelmatig updates verschijnen als er nieuwe ontwikkelingen in de techniek en/of in de literatuur zijn.
Voor de samenstelling van deze applicatie is gebruikt gemaakt van verschillende bronnen met uiteenlopende levels of evidence
Bronnen EvidenceBij de verslaglegging van letsels van het bewegingsapparaat dienen de volgende items beschreven te worden.
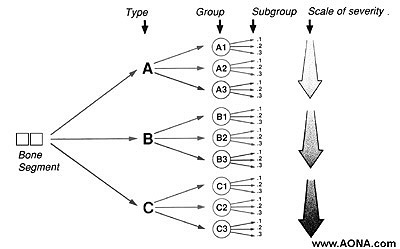
- Meest gangbaar is de classificatie volgens AO; codering voor achtereenvolgens bot; type; groep; subgroep.
Indien een patient poliklinisch behandeld kan worden dan moeten er duidelijke instructies gegeven worden over mogelijke complicaties, voornamelijk bij gipsimmobilisatie. Alarmsymptomen zijn;
In principe kan de patient na een week worden terug gezien op de polikliniek.
Indien een patient poliklinisch behandeld kan worden dan moeten er duidelijke instructies gegeven worden over mogelijke complicaties, voornamelijk bij gipsimmobilisatie. Alarmsymptomen zijn;
In principe kan de patient na een week worden terug gezien op de polikliniek. Tenzij er andere factoren zijn die eerder aandacht behoeven zoals hierboven beschreven of bij patienten na een operatie: controle van de weke delen, twijfel over het behoud van de stand van de fractuur of doorgelekte verbanden.
Bij pijn moet de patient altijd gezien worden en uitgesloten worden dat er complicaties zijn zoals drukplekken, te strak (circulair) gips, of ernstige complicaties zoals compartimentsyndroom of dystrofie.
Poliklinische fysiotherapie wordt in principe alleen voorgeschreven als er onvoldoende progressie in de beweging is 3 weken na (oefenstabiele) osteosynthese of het verwijderen van het gips.
- Bij boven- en onderbeensgips thromboseprofylaxe (bij voorkeur Fraxiparine)
- Bij het meer dan 5 dagen onbelast houden van een extremiteit
Referentie
1. Testroote M, Stigter W, de Visser DC, Janzing H. Low molecular weight heparin for prevention of venous thromboembolism in patients with lower-leg immobilization. Cochrane Database Syst rev. 2008 Oct 8;(4):
Het verwijderen van osteosynthese materiaal is niet risicoloos en dient daarom alleen op indicatie te gebeuren na goed overleg met de patient. (NB op dit moment loopt er een Nederlandse prospectieve multicentre clinical cohort studie die oa de klinische uitkomsten van het verwijderen van osteosynthese materiaal analyseert (3))
Indien een patient poliklinisch behandeld wordt dan moeten er duidelijke instructies gegeven worden over mogelijke complicaties, voornamelijk bij gipsimmobilisatie. Alarmsymptomen zijn;
1. toenemende pijn
2. toenemende zwelling of verkleuring van de tenen of vingers
3. gevoelsvermindering
In principe kan de patient na een week worden terug gezien op de polikliniek, zowel postoperatief als na conservatieve (gips) behandeling.
De meest voorkomende plek voor het ontwikkelen van een compartimentsyndroom is in het onderbeen (anticus loge), maar theoretisch kan het in elk afgesloten compartiment voorkomen inclusief handen, voeten en abdomen.
Het wordt veroorzaakt door ischaemie als gevolg van een toegenomen druk in het compartiment door bloedingen of oedeem. Die toegenomen druk kan uiteindelijk hoger worden dan de perfusiedruk van de capillairen waardoor de ischaemie ontstaat.
De eerste verschijnselen zijn sensibilitietsstoornissen omdat het zenuwweefsel het meest gevoelig is voor ischaemie (eerst sensibel, later pas motorisch). De ischaemie van de spieren die uiteindelijk ontstaat, leidt tot zeer heftige pijn.
Anticusloge:
Sensibilieteisvermindering in de 1e webspace van de voet en/of extreme pijn in de anticusloge (spontaan of bij bewegen van de hallux en heftiger dan alleen door het oorsponkelijke letsel te verklaren), zijn aanwijzingen voor een compartimentsyndroom. Bij de niet aanspreekbare patient kan een logedruk gemeten worden.
Logedruk:
Er zijn verschillende meningen over welke logedruk bij de meting geaccepteerd moet worden. Mubarak beschrijft een absolute druk van 30mm Hg als maximale grens (1). Hierboven dient een fasciotomie verricht te worden.
McQueen echter hanteert een drukverschil tussen de diastolische en de logedruk(2). Indien het verschil van de drukken groter is dan 30mmHg kan een fasciotomie achterwege gelaten worden zonder verlies van spierfunctie. De verschillende bevindingen worden opgesomd in het artikel van Taylor(3).
Behandeling:
Een compartimentsyndroom is een spoedindicatie voor een operatie. De behandeling bestaat uit het verrichten van een dermatofasciotomie. Voor een compartimentsyndroom van het onderbeen dienen altijd alle 4 de compartimenten geopend te worden.
Referenties
AO classificatie type 12
Volledige humerus inclusief aangrenzende gewrichten, AP en lateraal
In principe conservatief. Behandeling duurt lang; 10-16 weken (gemiddeld 10,7 weken, met een succespercentage van bijna 95% (7)). Sling of mitella of volgens Sarmiento methode (6). Na 3 weken functioneel behandelen, met sling of in brace. Volledige belasting op de elleboog en actieve beweging van de schouder uitstellen tot na volledige genezing van de fractuur.
Er zijn aanwijzingen dat een plaatosteosynthese de voorkeur heeft boven een intramedullaire pen (1), maar anderen weerleggen dit (2) omdat er bij de intramedullaire pen minder risico op infectie zou zijn en een snellere functioneel herstel. Een recent overzicht zet de voor- en nadelen op een rij(3). Bij graad 3 gecompliceerde fracturen kan voor een tijdelijke fixateur externe gekozen worden. Bij een intramedullaire pen kan sneller gemobiliseerd worden.
Conservatief:
Indien brace dan deze gedurende 8 -12 weken afhankelijk van de genezing. Oefenen vanaf 3 weken. Controlefoto op 1,3,6 en 12 weken.
Operatief:
Controlefoto na 1 week gevolgd door functionele behandeling. evt. eerste week collar and cuff. Volgende controlefoto na 6 weken en dan de belasting opvoeren.
· Uitval van de nervus radialis. Primaire uitval op zichzelf is geen operatie-indicatie, omdat het meestal berust op een tijdelijk probleem . De spontane genezingskans bij conservatieve behandeling ligt rond de 70% (5). Pas na 4 maanden een EMG laten verrichten om de definitieve schade te bepalen. Nervus radialis uitval in combinatie met een open fractuur is wel een operatie-indicatie.
Biomet suggestie
AO classificatie type 21
X-elleboog, AP en lateraal.
Conservatief:
Alleen de niet-gedisloceerde fractuur met intakte strekfunctie.
Behandelen met bovenarmsgips in 45° gedurende 4-6 weken
Operatief:
Gedisloceerde fracturen. Zuggertung osteosynthese en bij de distale of complexe (bv multifragmentaire) fracturen een hoekstabiele plaat osteosynthese (3). Het wordt geadviseerd om bij de Zuggertung de K-draden transcorticaal te plaatsen ipv intramedullair (1)
Conservatief:
Post-operatief:
Wheeless' Textbook of Orthopaedics.
Regan & Morrey (1)
X-elleboog AP en lateraal. Zo nodig CT-scan
Conservatief:
Type 1: Bovenarmsgips voor 2 weken
Operatief:
Type 2 en 3: Repositie en interne fixatie. Indien de fixatie niet stabiel lijkt dan tevens bovenarmsgips voor 6 weken
Conservatief:
Operatief:
Wheeless' Textbook of Orthopaedics.
X-elleboog AP en lateraal. Eventueel radiuskopdetail (3/4). Zo nodig CT.
Conservatief:
Operatief:
Conservatief:
Operatief:
Wheeless' Textbook of Orthopaedics.
X-schouder AP en axiaal en laagdrempelig een CT-scan.
Prognostisch ongunstige kenmerken (4):
Conservatief:
Operatief:
Algemeen: Het is nog steeds onduidelijk of een osteosynthese uiteindelijk een beter uitkomst geeft ten opzichte van een conservatieve behandeling (3). Op dit moment lopen er verschillende prospectieve studies die dat mogelijk zullen gaan ophelderen (5,6)
Conservatief:
Operatief:
AO classificatie type 13
X elleboog, AP en lateraal, eventueel CT scan
Conservatief:
Operatief:
Conservatief:
Operatief:
Wheeless' Textbook of Orthopaedics
X-schouder: AP, lateraal en axiaal
Conservatief:
Operatief:
Conservatief :
Operatief:
Volgens Ogawa (1): de fractuur wordt beschreven in relatie tot het coracoclaviculaire ligament :
X-Schouder: AP, lateraal en axiaal
Conservatief:
Operatief:
Conservatief :
Operatief:
X-Scapula: AP, lateraal en axiaal. Eventueel CT-scan
Conservatief:
Operatief:
Conservatief :
Operatief:
Wheeless' Textbook of Orthopaedics
Volgens Ideberg (1):
X-schouder: AP, lateraal en axiaal. CT-scan bij onvoldoende informatie over fracturering of bij twijfel over de operatieindicatie.
Conservatief:
Behandeling met 6 weken mitella kan gehanteerd worden voor bij de volgende situaties
Operatief:
Behandeling met
interne fixatie bij de volgende situaties
Conservatief :
Operatief:
AO classificatie type22
X-onderarm: AP en lateraal
Conservatief:
Operatief:
Conservatief :
Operatief:
AO classificatie type 23
X- pols AP en lateraal (Normale anatomie: Medoff RJ)
Conservatief:
Operatief:
Conservatief :
Operatief:
X-hand AP, lateraal en gerichte straal opname
Conservatief:
Operatief:
Conservatief :
Operatief:
Conservatief:
Operatief:
Conservatief :
Operatief:
Conservatief:
Operatief:
Conservatief :
Operatief:
Volgens Green & O'brien (1):
X duim: AP, lateraal
Conservatief:
Operatief:
Conservatief :
Operatief:
Referenties
geen
X-vinger AP en lateraal (incl. MCP gewricht). Let op intra-articulaire dislocatie en comminutie.
Conservatief:
Operatief:
Conservatief :
Operatief:
volgens Herbert(1):
X-pols: AP en lateraal en scaphoïdserie. Bij type B4 ook bedacht zijn op mogelijke perilunaire luxatie. Bij twijfel verdient een scintigrafie de voorkeur boven een MRI (2)
Conservatief:
Operatief:
Conservatief :
Operatief:
Geen
X-pols: AP en lateraal en scaphoïdserie. Bij twijfel kan een CT-scan overwogen worden
Conservatief:
Operatief:
Conservatief :
Operatief:
Conservatief:
Operatief:
Conservatief :
Operatief:
Conservatief
Operatief
Conservatief :
Operatief:
X-bekken: AP, ala en obturator. CT-scan laagdrempelig
Conservatief:
Operatief:
Conservatief :
Operatief:
Conservatief:
Operatief:
Conservatief :
Operatief:
AO classificatie type 31
Operatief (er is geen conservatieve therapie):
Operatief (er is geen conservatieve therapie):
Conservatief:
Operatief:
Conservatief :
Operatief:
Onderscheid maken tussen
Conservatief:
Operatief:
Conservatief :
Operatief:
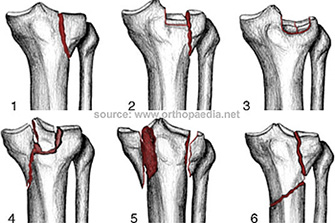
Conservatief
Operatief
Conservatief:
Operatief:
Beeldvorming
Conservatief:
Operatief:
Conservatief:
Operatief:
De duur tot genezing bij tibiaschachtfracturen is zeer lang. Voor de stabiele fracturen gemiddeld 20 weken, voor de instabiele fracturen >30 weken!
Conservatief:
Operatief:
Conservatief:
Operatief:
Conservatief:
Operatief:
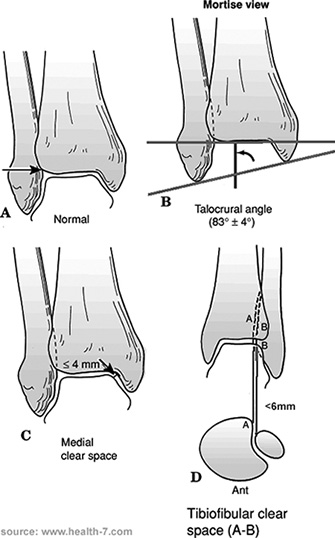
Conservatief:
Operatief:
Conservatief:
Operatief:
Volgen Hawkins (1):
Conservatief:
Operatief:
Conservatief:
Operatief:
Opmerking:
Conservatief:
Operatief:
Conservatief:
Operatief:
Conservatief:
Operatief:
Conservatief:
Operatief:
Conservatief:
Operatief:
Conservatief:
Operatief:
Conservatief:
Operatief
Conservatief
Operatief:
Conservatief:
Operatief:
Conservatief, behalve bij cardiologische indicatie (cor-contusie) kan een opname overwogen worden
Conservatief:
Operatief:
Conservatief:
Operatief:
Geen garanties
Geen enkele informatie verstrekt door deze app zal enige vorm van garantie geven. Inter-Med is niet aansprakelijk voor ongewenste uitkomsten of effecten voortvloeiend uit de toegepaste behandeling. Daarnaast garandeert Inter-Med geen enkel resultaat bij het implementeren van de in deze app voorgestelde techniek of behandeling. Inter-Med kan niet aansprakelijk gesteld worden voor materiële schade, verlies van praktijk, immateriële schade, rechtszaken of verlies van inkomsten.
Link Disclaimer
Links zijn toegepast als informatieve bronnen. De meeste links zijn externe links en worden derhalve niet onderhouden door Inter-Med. Deze links worden enkel aangeboden als extra service op de website. De inhoud van de gelinkte sites valt buiten de verantwoordelijkheid van Inter-Med.
Fouten en Veranderingen
De inhoud van de app kan technische onjuistheden of tikfouten bevatten. Dientengevolge is Inter-Med niet aansprakelijk in geval van fouten in de tekst, foto's of illustraties. Daarnaast kan zonder melding de inhoud gewijzigd worden.
Copyright and intellectueel eigendom
Copyright is van toepassing op alle tekst, illustraties en foto's op de site. Copyright is ook van toepassing op het concept van het klikbare skelet als toepassing voor de behandeling van botbreuken. Het gebruik door derden van elke informatie op de website is verboden tenzij vooraf schriftelijke toestemming is verkregen van Inter-Med.
Ethische aspecten
Inter-Med hanteert de ethische principes voor wat betreft het gebruik van medische informatie en voorzieningen, specifiek gericht op het internet.
Gebruikers verantwoordelijkheden
De informatie in deze app kan niet gebruikt worden ter formulering van een diagnose of behandeling, of voor het beargumenteren om medicatie te starten danwel te stoppen, zonder tussenkomst van een dokter. De in deze app voorgestelde techniek kan nooit een vervanging zijn van een consult, onderzoek of diagnose door een dokter. Daarnaast mag de informatie in deze app niet gebruikt worden om een bepaalde techniek te promoten.
De gebruiker is bewust van het feit dat de informatie in deze app niet compleet kan zijn.
Financiele aspecten
De inhoud van deze applicatie is volledig onafhankelijk samengesteld, zonder tussenkomst van een commercieel bedrijf. De realisatie van de app en het gratis aan de gebruiker kunnen aanbieden is financieel mogelijk gemaakt door Biomet. Biomet heeft geen enkele inbreng gehad in de totstandkoming van de inhoud.
© 2014 - Inter-Med